
A : You can check out this clip to learn about INCOTERMS
A : A phytosanitary certificate is a document to be issued only by a public officer who is technically qualified and duly authorized by an NPPO of the exporting country that certifies that a plant or plant-based product is free of insects and pests and meets the requirements of the destination country.Therefore, the phytosanitary certificate is regarded as one of the most important documents in the import-export process
A : pls prepare below info before request booking

A : The tax that you must pay when import the goods is import duty and VAT but some kind of goods will include excise tax and interior tax.
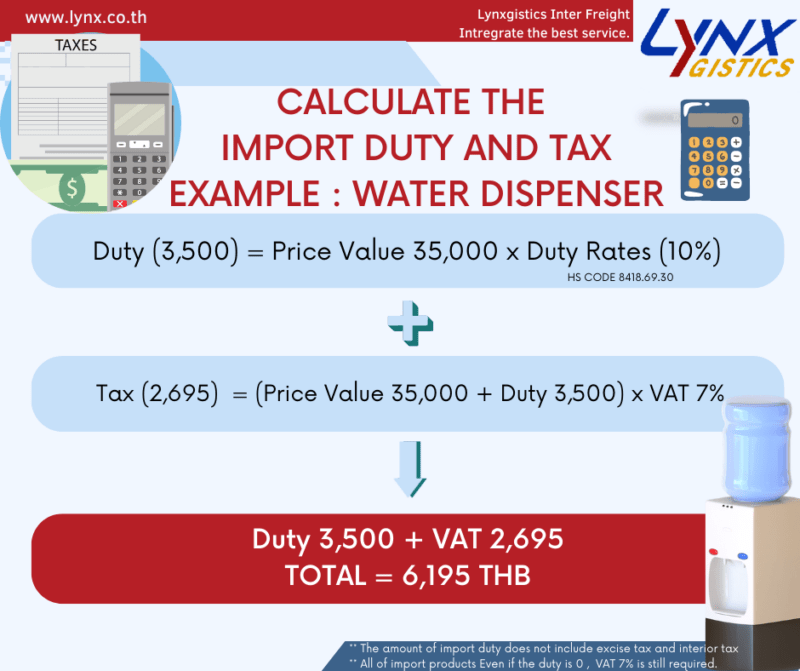
A : In case of importing from foreign countries, Section 8(3)
Importers are obligated to pay taxes at the specified rate. By calculating the excise tax as follows:
Excise Tax = (C.I.F Product Price) x Excise Tax Rate

A : Excise tax collection in Thailand It is a specific sales tax levied on certain goods and services. The objective is to allow consumers to bear higher tax burdens than usual. for products that may have a negative effect on consumer health or morals or products that look extravagant or goods that receive special benefits from the state or goods that cause a burden on the government to build various facilities to provide services to consumers or as a product that causes an impact on the environment
Goods and services that the Excise Department collects excise taxes are goods that the government wants to control consumption. Due to the nature that causes negative effects on health or affects the morals of the people. or looks like a luxury product or as goods and services that receive special benefits from state affairs which include the following products
Oil and oil products
Petroleum products include gasoline, kerosene, jet fuel, diesel, heavy fuel, fuel oil and other oils that is similar to the oil that has already been named
Beverage
Beverage According to the Excise Tax Act, B.E. 2560, beverage means something that is normally consumed as a beverage. Without additives, which are non-alcoholic or alcoholic. not more than 0.5% by volume, packed in containers and sealed but not as deep as water or natural mineral water Distilled or filtered water for drinking Without flavoring, fresh milk, other milk as specified in the law on food. Beverages that the manufacturer has produced for retail sales exclusively do not contain carbon dioxide.
Electrical appliances
Electrical appliances mean products that use electrical energy. and shall also include anything used in conjunction with electricity or relating to electricity such as air conditioners with cooling capacity not exceeding 72,000 BTU per hour and other electric lamps and chandeliers for ceiling or wall mounting. but does not include those used for Illumination for outdoor public spaces or highways.
Crystal lake glass and other crystal glass
Glass and glassware means articles and utensils made of glass such as glass, lead crystal and other crystal glass.
Cars (passenger cars, pick-up trucks, passenger cars with no more than 10 seats)
Motor vehicle, vehicle with three or more wheels and running on engine power, electric power, or other power but does not include vehicles that travel on rails motorcycles with sidecars of not more than 1 wheel, motorcycles under the law on cars and vehicles announced by the Minister.
Passenger car means a sedan or automobile designed for regular use. and shall include a vehicle in the same manner such as a vehicle with a homogeneous roof in a permanent manner on the side or behind the driver there is a door or window and a seat. regardless of how many seats there are
Pick-up truck means a vehicle that has the back as a pick-up truck. which is open to the rear of the car without a roof designed for vehicle weight total weight not exceeding 4,000 kg.
Passenger vehicle means a van or vehicle designed to transport a large number of passengers. as well as similar vehicles with seating for not more than 10 people.
Yachts and recreational water vehicles
such as Boats, yachts and all kinds of water vehicles
Perfume
perfume oil and fragrance oil. Aromatic products means perfumes, perfume oils, perfumed oils, and other aromatic substances, but excluding perfume oils that can be used exclusively for manufacturing products.
Carpets and other floor coverings (Only made of fur)
Carpets and other floor coverings Only made of fur means that the ramps are made of various materials. and textile products. It is a piece of fabric that contains 1 or more layers of woven material for the benefit of use. like a matting machine and general floor coverings and includes articles that resemble carpets and floor coverings but intended to be used for other purposes
Motorcycle
a vehicle with no more than two wheels. If there is a side trailer, there is not more than one additional wheel. Walking with engine power or electric power and shall include motorcycles according to the law on cars
Battery
a cell or a group of electrical cells connected in series or parallel or both and capable of storing energy and providing electrical energy.
Entertainment or leisure business
the business operation in terms of entertainment or recreation in service places for the purpose of earn money as a business such as theatrical venues, movie venues, nightclubs, cabarets, discotheques, karaoke, cocktail lounges, a place to bathe or steam and massage etc.
Gambling business
the business operation in the area of providing gambling by any means. In order to receive prize money or other benefits such as horse races, government lottery, etc.
Businesses that receive concessions from the state.
It means that any business in the form of providing services to the general public with permission or concessions from the state to operate, such as telecommunications, etc.
Liquor
All objects or mixtures containing alcoholic beverages that are consumed. as well as liquor or inedible water. But when mixed with water or other liquids, it can be drunk and eaten just like liquor. Soaked liquor means undistilled liquor and shall include fermented liquor mixed with liquor but there is also a strong alcohol of no more than fifteen degrees as well, such as beer, wine, etc.
Tobacco
Tobacco leaves or compressed tobacco that have been cut into strips and dried.
Playing cards
According to the Playing Cards Act, BE 2486, Section 4, means playing cards made of paper or leather or made of other objects as prescribed in the Ministerial Regulations, and in Section 7, no person shall make playing cards or bring in playing cards. unless authorized by the Director-General, and in Section 7, no person shall sell playing cards in trade unless authorized by the Official In issuing a license, the applicant must pay a fee as prescribed in the Ministerial Regulation.At present, tax is only collected on imported playing cards. Importers must bring excise stamped playing cards and pay a fee of not more than 30 percent depending on the type and object made, and put the stamp on the envelope of the playing card that has been paid.
For playing cards produced within the country, there is no tax collection because the playing card factory is a state-owned enterprise. under the Excise Department will be the sole monopoly on the production of playing cards
REF
https://webdev.excise.go.th/aec-law/th/excise-th-thailand.php
https://ms.udru.ac.th/FNresearch/assets/pdf/ch15.pdf
http://bta.excise.go.th/calculate_tax_car.php?calculate_id=0002
A :

MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheet) a document that shows information about chemicals or chemicals about their hazards, toxicity, usage, storage, transportation, disposal and other handling. To ensure the correct and safe handling of chemicals.
At present, according to the United Nations Announcement on the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS), SDS is required as one of the elements in communicating information on chemical substances. from on the label and to achieve consistency and the same system Therefore, it is called the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) with the form and information in the SDS set for 16 topics, with the following topics:
1. Identification of the substance/preparation and of the Company/undertake
2. Hazards Identification

3. Composition/Information on Ingredients

4. First Aid Measures
5. Fire Fighting Measures

6. Accidental Release Measures
7. Handling and Storage

8. Exposure Controls/Personal Protection

9. Physical and Chemical Properties
10. Stability and Reactivity

11. Toxicological Information
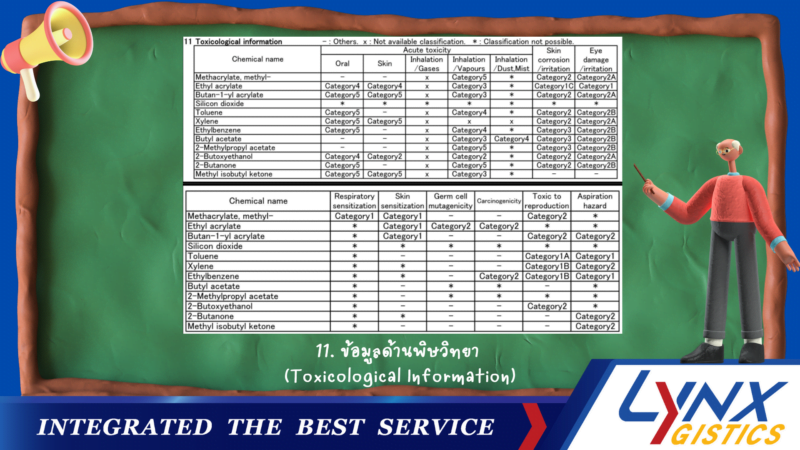
12. Ecological Information

A : 
CITES stands for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention. The convention became effective on July 1, 1975.
The convention has 184 parties as of August 2022, including 183 states and the European Union. Thailand is the 80th member to ratify the Convention, which was signed in 1975 and ratified on January 21, 1983.
The purpose of CITES
The purpose of CITES is to protect endangered wild animal and plant species by establishing a framework for countries to collaborate in order to ensure that plant and animal species do not become depleted due to international demand. However, Domestic trade within a country is not regulated by CITES, even if the species is on the CITES list.

How CITES works
CITES regulates international trade in species of wild animal and plant, i.e., export, transit, re-export, and import of live and dead wild animals and plants, as well as parts and derivatives thereof, through a system of permits and certificates that can be issued if certain conditions are met and must be presented before leave or enter a country.
The CITES appendix
The list of species on the CITES list is determined using scientific data, both taxonomy and Biological Parameter, such as population status, population trends, and distribution. Distribution, habitat availability, geographic trends, and threats are identified, and commercial use and legal status must be considered.
There are three appendices to CITES that guide international trade based on how threatened each species is with extinction.

– Appendix 1 offers the highest level of protection and includes species that are closest to extinction. These species can’t be legally traded, except under special circumstances like scientific research.
Examples of wild animals on this list include: Red panda (Ailurus fulgens) Gorillas (Gorilla gorilla) Chimpanzee (Pan spp.) Tiger (Panthera tigris subspecies) Asiatic lion (Panthera leo persica) Leopard (Panthera pardus) Jaguar (Panthera onca) Cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus) Asian elephant (Elephas maximus) African elephants (Loxodonta africana) Asian arowana (Scleropages formosus) Jullien’s golden carp (Probarbus jullieni) etc.
Examples of wild plants on this list include: Pigeon orchid (Dendrobium cruentum) etc.

– Appendix 2 includes plants and animals that are likely to be threatened with extinction if trade isn’t regulated. It also includes “look-alike” species that are similar to those listed in the appendices. International trade is permitted for plants and animals included in Appendix 2, but is monitored, limited and controlled with permits.
Examples of wild animals on this list include: Savannah monitor (Varanus exanthematicus) Great white shark (Carcharadon carcharias) American black bear (Ursus americanus) Hartmann’s mountain zebra (Equus hartmannae) Grey parrot (Psittacus erithacus) Green iguana (Iguana iguana) Queen conch (Strombus gigas) American paddlefish (Polyodon spathula) etc.
Examples of wild plants on this list include: Guaiac wood (Guaiacum officinale) Siamese rosewood (Dalbergia cochinchinensis) etc.

– Appendix 3 includes species that are protected by at least one country, which requests cooperation from other governments to ensure that trade doesn’t threaten their survival.
Examples of wild animals on this list include: Hoffmann’s two-toed sloth (Choloepus hoffmanni) African civet (Civettictis civetta) Alligator snapping turtle (Macrochelys temminckii) etc.
Examples of wild plants on this list include: Gnetum montanum Markgr etc.
Reference:
- Website of The Forest Industry Organization (www.fio.co.th)
2. Website of International Fund for Animal Welfare (www.ifaw.org)
A : The packaging used to contain dangerous goods must be good quality and completely sealed to prevent the leakage of dangerous goods during transportation, which may cause vibration, temperature change, humidity or pressure. The form of the packaging is in accordance with the nature and status of the hazardous substance being packaged, which can be divided into 3 types:
- Characteristics of package type is a product that is completely packaged. The goods contained within are ready to be delivered. Can act to completely conceal the contents and includes gas containers and items of any mass or nature that can be transported without packaging or transported by placing it on a litter in crates or in other handling equipment. The transport of radioactive materials, dangerous goods transported in bulk or in tanks are not included.
Dangerous goods are classified into packing groups based on the hazard level of the substance as follows:
Packing group I: Substances with a high degree of hazard.
Packing group II : Substances of medium hazard class.
Packing group III: Substances of low hazard class.
The letters representing the packing group are:
X for packing group I, II and III
Y for packing group II and III
Z only for packing group III
- Characteristics of packaging type is one or several containers, including components or materials necessary for the purpose of containment of hazardous substances and perform safety functions.
IBC (Intermediate Bulk Container) packaging is the packaging that moveable, stable or flexible. Capacity depends on packing group and hazardous material status. Designed to be transported by machines. Tested to withstand the stresses caused by handling and transport in accordance with standards related to the transport of dangerous goods by road with the following features:
- Capacity not more than 3.0 cubic meters (3,000 liters) for solids and liquids of packing group II and III.
- Capacity not to exceed 1.5 cubic meters for solids of packing group I when packed in IBC made of plastics, composites, fibreboard and wood.
- Capacity not more than 3.0 cubic meters for solids in packing group I when packed in metallic IBC.
- Capacity not more than 3.0 cubic meters for radioactive material type 7
Large packaging is a packaging that contains outer packaging, which contains items or packages contained within. Designed to be lifted or moved by machine and having a net weight of more than 400 kilograms or having a capacity of more than 450 liters but with a volume not exceeding 3 cubic meters.
- Characteristics of the tank type is a hazardous substance container that is equipped with structural equipment and related equipment.
- Tank Container is a walled tank with structural equipment and related equipment such as equipment used for lifting or moving for gas, hazardous, liquids transportation and materials in the form of powder or granules and has a capacity of more than 450 liters.
- Portable tank is a liftable and movable tank used for multimodal transport with a capacity of more than 450 liters, which includes all necessary equipment for transport.
Conditions of information that must be posted on dangerous goods packaging.
On dangerous goods packaging it is necessary to display the UN number, chemical name, primary risk label, subsidiary risk label and a certified UN mark.
A : UN mark is an international system created by the United Nations to classify packaging that can contain liquid and solid hazardous materials for safe air, road and sea transportation. The United Nations has issued requirements for the testing and certification of hazardous materials packaging. This requirement applies to packaging, IBCs and portable tanks. Standardized packaging must display the symbol, code, letter indicating the packing group, date of manufacture, packaging manufacturer code, maximum capacity test results, country codes and packaging certifying bodies.
UN Mark cannot be used for transport in different transport sectors, for example, the packaging of dangerous goods used for sea transport is the responsibility of the Marine Department to certify. But this packaging cannot be used for air transportation. Because the law does not have the authority to certify packaging for air transport.


